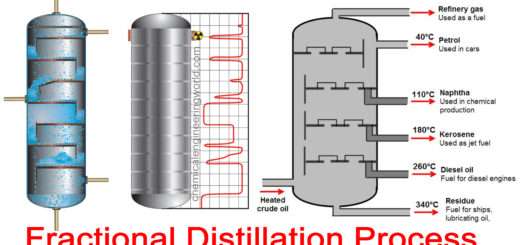
BUBBLING FLUIDIZED BED REACTOR
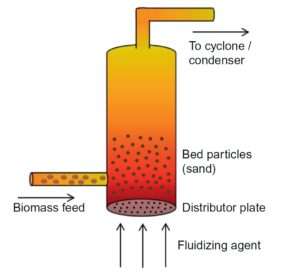
A fluidized bed consists of a bed of particles that’s unbroken fluidized by the continual
upward flow of a gas. Typically, the process consists of a vertical cylindrical tube
with a perforated distributor plate at the lowest. Some material in particulate type
(usually sand) is placed within the tube, and gas flows from the distributor plate upward. If the speed of the gas is tiny, it’ll merely flow round the particles and leave at the highest. At this case, we’ve what’s known as a fixed bed. If the gas rate keeps increasing, at some Location the force exerted upwards on every particle equals
the particle weight. in this scenario, the particle is suspended and also the gas rate is
called minimum fluidization rate. Any extra increase in rate creates
bubbles of gas that quickly flow upward within the system. this is often known as a bubbling fluidized
bed. A bubbling fluidized bed is shown in Figure below.
The bubbling fluidized bed presents many vital characteristics: the extreme
movement of the particles promotes smart inter-mixture and uniform conditions throughout
the bed, therefore heat transfer is extremely economical and temperature management is easy.
This system is well tried commercially, and scale-up is straightforward. Specifically for quick
pyrolysis, the short duration of the vapors is controlled just by variable the gas rate.

The bubbling fluidized bed is doubtless the foremost standard reactor
for quick shift. the most disadvantage with fluidized-bed reactors is that they
require fairly little particles (2–3 mm) to reduce heat/mass transfer effects: this
leads to costly needs for grinding lignocellulosic biomass.