Solenoid Valve Working and Types
Solenoid Valve Working and Types
Solenoid Valve Working and Types
A Solenoid valve opens and closes by an electromagnetic force so it is also called an Electromagnetically operated valve. If initially, the valve is in close condition then after application of electromagnetic force it will lift the plunger and the valve opens. It is an automatic valve. Different types of solenoid valves are available in the market based on application.
What is a solenoid?
It is a very simple invention of physics. It is nothing but the hollow cylinder of thin wire. When the current is passed through the wire that system will act as a magnet. This magnetic field will be used to do many tasks. The higher the current passes higher will be the magnetic effect. Nowadays it is used in almost every electronic appliance.
Parts of the solenoid valve
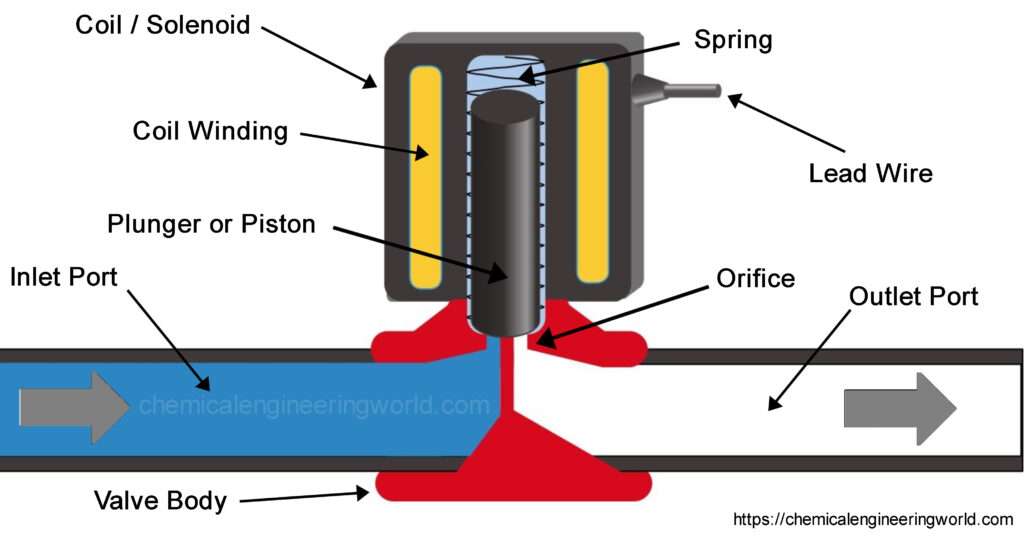
- The valve body is the part of the valve which is connected to the pipe from which fluid is flowing. It is the primary pressure boundary. It contains the whole solenoid assembly inside it.
- The inlet port of the valve is the entry point of the fluid to the valve.
- The outlet port is the exit point for the fluid which is allowed by the automatic valve to flow. It exits from the valve through the outlet port and goes to the further process plant via piping.
- The Coil winding is the long thin wire which is wounded around the magnetic core.
- The plunger is the part that stops or starts the flow of fluid. When the solenoid is energized the plunger will move up or down based on design and let the fluid flow. It is made up of ferromagnetic material. Usually, it is cylindrical.
- The solenoid coil is the part of the valve which energizes and lifts the plunger. It is a hollow cylinder of thin wire.
- The spring keeps the plunger in position when the current is not flowing in the solenoid. When the current is flowing in the wire the plunger will act against the spring action and opens the valve. So, after that when we want to close the valve we need to put the plunger back to its correct position at that time spring will do it for us.
- The orifice is the hole through which fluid will flow from the inlet port to the outlet port. At the close condition, the plunger will stop the flow by blocking the orifice.
Working of the Solenoid valve
As it is an automatic valve first we need to understand when we need to open and close the valve. When the sensor senses that we need fluid on the outlet side the current will flow in the solenoid and due to which the plunger will act against spring and lift from the orifice. This will allow the fluid to flow. After the sensor senses that enough quantity of fluid is taken then it will stop the current and due to which the plunger will again chock the orifice and closes the valve.
In the case where we need more flow of fluid then the sensor will send the message to the power system and it will pass more current. Due to an increase in current, the magnetic field will increase and the plunger will lift more than the previous lift which will allow more fluid to flow through the orifice. So, based on the requirement sensor passes the current and according to that plunger will lift.
Types of Solenoid valve
Direct Acting Solenoid valve:
It is the simplest type of solenoid valve. It does not require any external force to open and close the valve. It is very fast-acting than other types. It is usually of two types one is NC (normally close) and the other is NO (normally open). In NO valve plunger is in an open condition in the absence of current flow as the current flows it will chock the orifice by the plunger and stops the flow of fluid. The exactly opposite process happens in the NC valve.
Pilot operated solenoid valve:
It is a more complex type of solenoid valve. Here we are introducing a diaphragm inside the valve. In this valve, we are separating the inlet port and outlet port by the diaphragm. Above the diaphragm, there is one chamber that is always pressurized by inlet fluid and keeps the diaphragm in close condition. As the solenoid is energized it will lift the plunger due to that the pressure inside the chamber above the diaphragm will reduce. After that due to pressure reduction in the chamber diaphragm will open and the flow of fluid will start. Refer to the video below to understand the working of the valve. It requires less power than a direct-operated solenoid valve.
Two-way Solenoid valve:
It contains two openings for the flow of fluid. It is in normally close condition as the current flows plunger will lift and fluid will pass.
Three-way solenoid valve:
It contains three openings and two orifices inside the valve. Orifice opens and closes alternatively. Two different designs are available 1) Two inlet opening ports and one outlet port 2) Two outlet ports and one inlet port. The first one is used when we need to mix two liquids and the second is used when we need to separate one stream into two.
Four-way solenoid valve:
It contains two pressurized inlet ports and two exhaustive outlet ports.
Solenoid Valve Applications
- In the refrigeration system
- Industries where compressed air is not used
- Vacuum system
- Automobile systems
- Etc.
Advantages
- Fast opening
- Low power consumption
- Compatible with AC and DC both
- Can be installed vertically and horizontally
Disadvantages
- Very sensitive to voltage
- The magnetic field affects valve opening and closing
- Need to replace coil after some time
Reference:- doityourself, startersolenoid, brighthubengineering, omega