Rotameter Working and Types
Rotameter Working and Types
Rotameter Working and Types
Rotameter is a device which is used in chemical and related industries in order to measure the flow rate or average velocity of the flowing fluid.
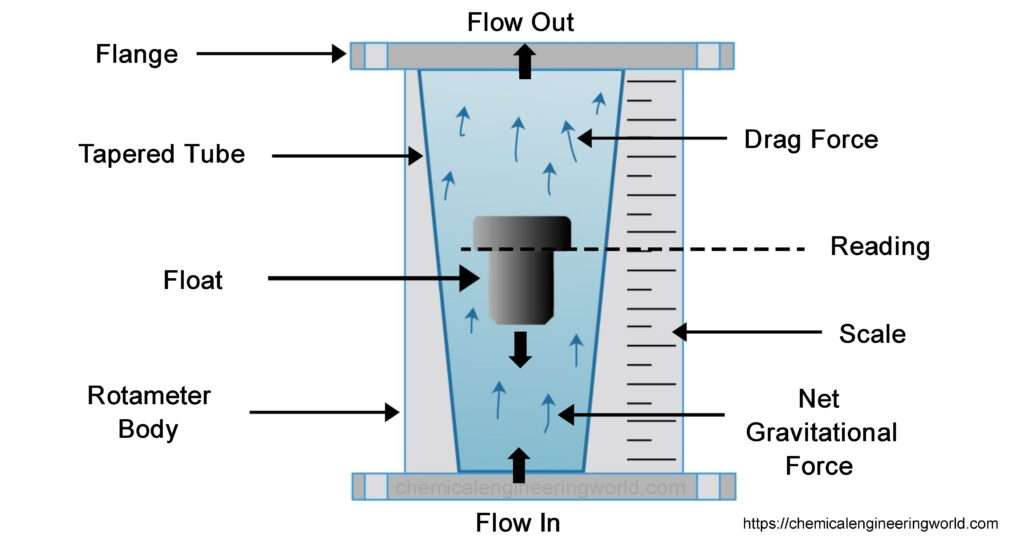
Rotameter is a simple equipment which consists of a tapered tube and a float. The float is placed inside the tube and usually nets are placed at both the ends of the tube. This arrangement can be connected with a pipe line with flanged connections. Rotameters are always installed vertically in the pipelines. A scale is marked on the tube to read the values of flow rate directly.
Rotameter Working
When the fluid is not flowing then the float rests at the bottom of the rotameter. The fluid is made to pass through the rotameter such that the direction of flow of the fluid is parallel to the axis of the rotameter.
The flow of fluid through the rotameter causes the float to move along with the fluid. There are two primary forces involved, an upward drag force due to the motion of the fluid in upward direction and a downward force due to gravity which is due to the weight of the float itself. When these forces are balanced then the float moves to a particular location in the tube and it stays right there because it has achieved dynamic equilibrium.
In case it happens that the flow rate of fluid flowing through the rotameter is very high then it may happen that the float may get swept along with the fluid. The nets attached to either side of the rotameter ensure that the float does not get carried away in the pipe line. If it happens then it may get stuck near a valve in pipeline and cause blockage or enter equipment down the line and cause it to malfunction. A down side of net is that if the flow rate of flowing fluid is very high then the float will get stuck near the net and act as a blockage for the fluid flow, this may cause the flanges to get weakened and the liquid may start showering at the site of rupture.
Types of Rotameter
- Glass Tube Flowmeters
- Armoured Purgemeter
- Flanged Armoured Rotameter
1. Glass Tube Flowmeters:
They are the most common type of rotameters which are used extensively not only in industries but also in pilot plants and labs to measure flow rates of wide variety of fluids, both liquids and gases.
2. Armoured Purgemeter:
One of the advantageous functionality is its ability to purge the fluid if the condition of the system is not proper. It is useful for low flow rate, high pressure and corrosive applications.
3. Flanged Armoured Rotameter
It is used in automated systems where the applications require quite opaque liquids at aggressive conditions. It is mostly used in high pressure applications.
Advantages of Rotameter
- It is simple to install and is easy and cheap to maintain.
- It has a linear scale over large range of flow rates.
- The pressure drop across the float is constant. Hence the pressure loss due to the float itself is quite small.
- Rotameters are very versatile, they can be easily sized or their use can be changed for different systems.
Disadvantages of Rotameter
- It requires a certain minimum magnitude of flow rate of fluid below which the float would fall and just stick to the rotameter.
- If opaque fluid is used then the scale is not properly visible, it may cause misreading the meter.
- It cannot be installed in a horizontal position.
- If flow rate of fluid is very high then glass tubes may be subject to breakage.
Reference:- instrumentationtools, automationforum, bucksales






























