Mixer-Settler Working Principle

Mixer-Settler Working Principle:- Extraction is a process in which the components of interest in a liquid mixture are separated by contacting the feed liquid mixture with another liquid called solvent and mixing both the liquids thoroughly. The components of the feed liquid mixture will redistribute themselves between the feed itself and the solvent.
The purpose of extraction can be either to remove impurities from the feed liquid mixture or to separate the valuable components from the feed liquid mixture.
Mixer-Settlers are one of the oldest types of extraction equipment. Mixer-Settlers come in all kinds of shapes and sizes but as the name indicates their defining feature is that they are a combination of mixers and settlers.
Various Sections in Mixer-Settlers
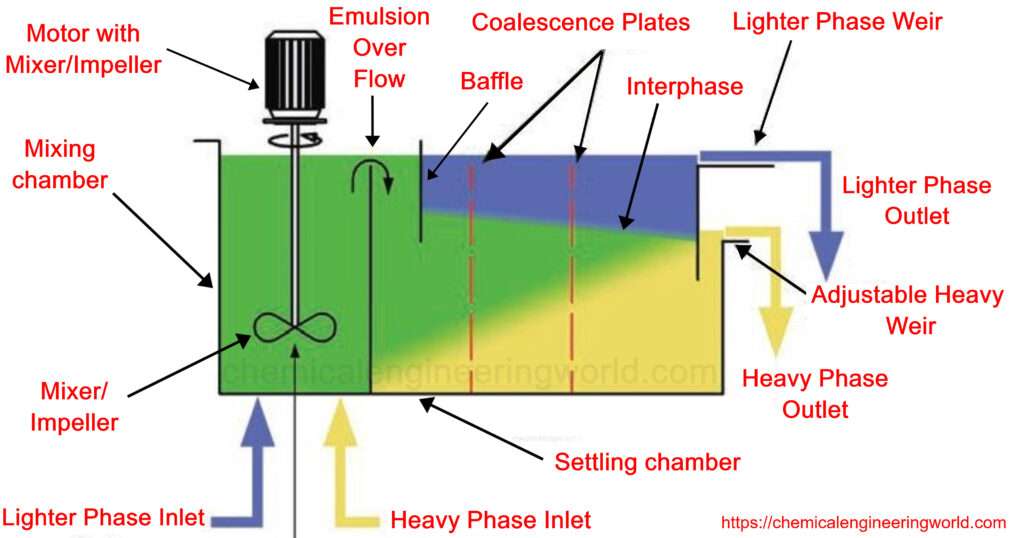
- Mixing Section: It is the part of the equipment which has at least two inlet pipes. One pipe for the feed and the other pipe for the solvent. This section is a chamber in which two fluids get into contact and an agitator is installed in order to mix the liquids thoroughly. Baffles are also installed so that mixing is efficient and the vortex is eliminated.
- Settling Section: It is the part of the section where the mixed liquids enter in order to separate into two different phases based on density differences and there are weirs in order to separate both the phases.
- Recirculation pipelines: some part of the separated phases may be taken and fed back to the mixing section in order to maintain the ratio of the feed and the solvent.
Working of the Mixer-Settler Equipment
The feed liquid mixture is usually called the Aqueous and the other liquid which is introduced to separate components is called Solvent and usually it is organic in nature. The Aqueous and the solvent should be immiscible with each other to a great extent such that only the component of interest must get redistributed among both the phases.
The Aqueous solution and the Organic are fed into the mixing section where they are thoroughly mixed. The mass transfer of the component of interest (Solute) from the aqueous phase to the organic phase occurs in this section. The mixture of the Aqueous phase and the Organic phase is called an Emulsion.
This Emulsion enters into the Settling section and if the density differences between both the phases, aqueous and organic is large enough then the separation of the phase happens just by gravity and it takes very less time. If the density and surface tension differences of both the liquids are not large enough then the emulsion will take a lot of time to separate. This increases the size of
the settler section and often makes the extraction process infeasible for industrial use in continuous process.
In case emulsion takes a large time to separate then obstructions called gates can be used in order to separate both the phases and/or the temperature can also be increased as density of a liquid changes due to change in temperature.
The lighter phase liquid will rise to top and the heavier phase liquid will fall to bottom. They both have different weirs from which they are drawn and sent to next equipment or stored.
Sometime a fraction of the aqueous phase separated from the settler section is taken and fed back to the mixing section through recirculation pipes in order to act as a scrubber and also to maintain the organic to aqueous ratio.
Advantages of Mixer-Settlers
- The headroom required is less.
- Very high flow rates can be operated.
- Has capacity to provide long residence time.
- Small number of stages is required.
Disadvantages of Mixer-Settlers
- The floor space required is more.
- It is labour intensive equipment.
- Requires long settling time if density difference between liquids is small.
Reference/Image:- Wiki, Dedietrich
































