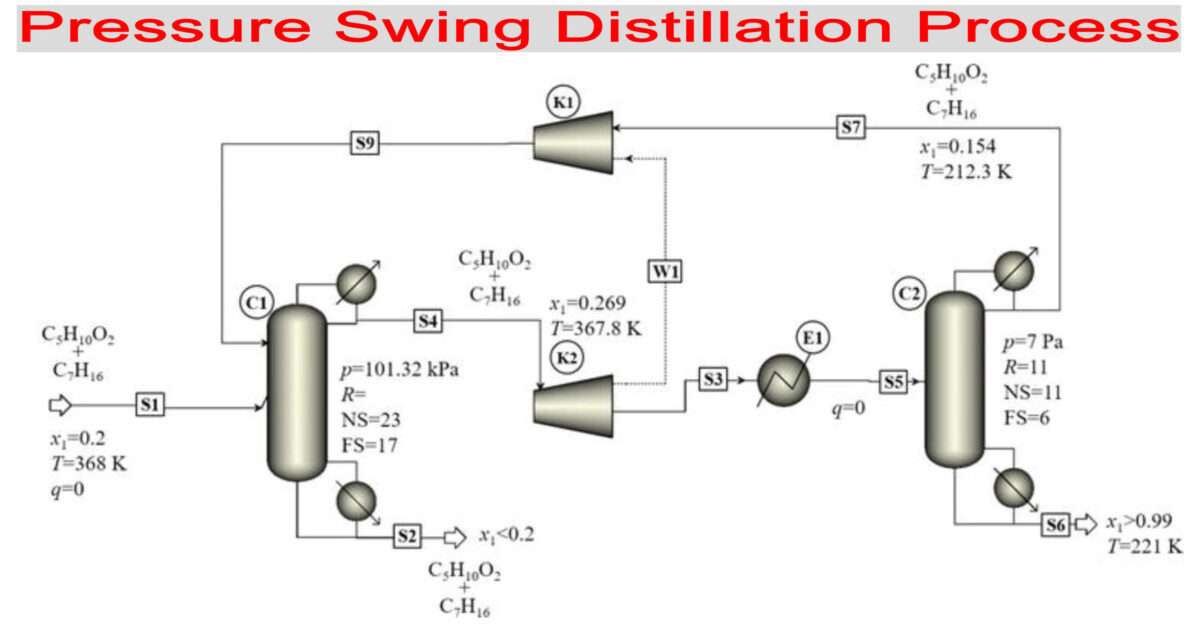
Adsorption and Applications

Adsorption operations exploit bound solids ability to preferentially
concentrate specific substances from solutions (gaseous or liquid) onto their surfaces.
Thus, by contacting fluids with such solids, the required objective of purification or
separation is also achieved.
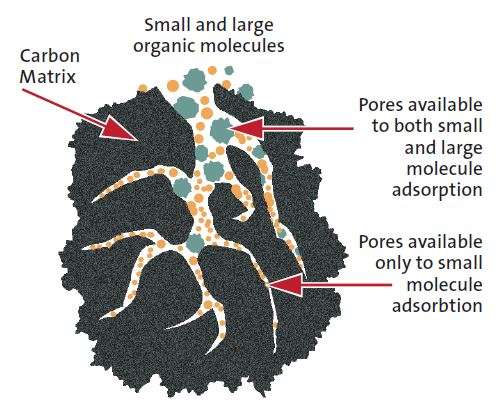
The extent of adsorption of a given scenario is reached once equilibrium is established
between the adsorbent and its contacting resolution. In apply, adsorption performance is also powerfully influenced by the mass transfer of the species between the solution and therefore the} adsorbent surfaces and also the adsorption reaction rate. Technically, adsorption is, therefore, an equilibrium-diffusion-reaction method
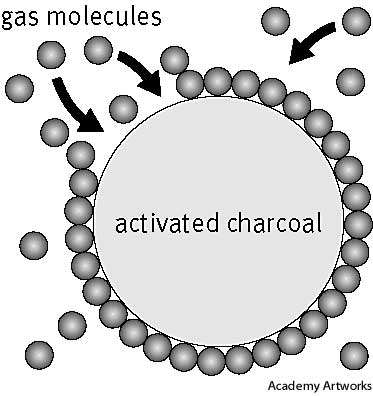
APPLICATIONS
Recorded application of charcoal for purifying water 2 millennia past was found in
Sanskrit manuscripts: “It is nice to stay water in copper vessels to expose it in daylight
and to filter it through charcoal” (Weber, 1984). trendy use of adsorbents began with
the discovery of the de coloring result of charcoal on solutions (Lowitz, 1786), followed
by the invention of a charcoal cartridge for private protection throughout The 1st World
War. With the increasing availableness of various kinds of adsorbents today, and the
more recent interests in biotechnology and green technology, there has been an excellent
expansion within the applications of adsorption in several areas. A partial list of adsorption
applications follows.

For liquid-phase adsorption
• De coloring, drying, or de gumming of petroleum product
• Removing of dissolved organic species from water provides
• Removing odor, taste, and color from water Flow
• Advanced treatment of waste water (domestic and industrial)
• De coloring of crude sugar syrup and vegetable oils
• Recovery and concentration of proteins, pharmaceuticals, and bio-compounds from
dilute suspensions
• Bulk separation of paraffin and ISO-paraffin
For gas-phase adsorption
• recovering organic solvent vapors
• Dehydration of gases
• Removing harmful agents and odor for personal protection
• Air separation
• Separating traditional paraffin from ISO-paraffin aromatics
• CO2 capture for addressing temperature change