Electrolysis Overview
Introduction:
In the 19th century, Electrolysis word initially came from the Scientist Michael Faraday. Electrolysis: Electrolysis word derived from the word Electro + lysis which means Electricity + Separation respectively.
Definition of Electrolysis:
- Electrolysis is the process in which chemical reaction is produced artificially (not naturally about to happen) using the electricity source type of D.C (Direct Current).
This D.C current purpose is to breakdown the complex constituents into simpler constituents by passing through the medium (I e. Electrical Energy acts as a deriving force for the production of chemical reactions).
Before starting the understanding of Electrolysis Mechanism, we need to learn about the basic related terms in electrolysis are following mentioned below:
Cations:
Cations are formed usually When metals donate electrons (may be one or more than one) from their shell (i.e. J, K, L, M electrons shells) to other atoms or molecules. Cations contain Positive charge with themselves. For Examples of cations are hydrogen (H+) & sodium (Na2+).
Anions:
Anions are formed in such case where non – metal elements accept the electrons from other donor atoms or molecules. Anions possess a negative charge. For Examples of anions are Chloride (Cl–) & hydroxide (OH–).
Electrolyte:
- An electrolyte is simply defined as the substance which has the ability to produce the electricity through the medium in which it is dissolved or added.
Dissolved medium may be water or aqueous solution. Medium should have a solvent ability to perform Electrolysis. Electrolytes consist of property in which they are decomposed into their constituents (uniformly divided into cations & anions throughout the solution). Example of Electrolyte: NACL, KCL, etc.
Non Electrolyte:
Compound which don’t conduct electricity neither in solid or aqueous state. Example of Non electrolyte are distilled water, alcohol, sugar, etc.
Electrodes:
Electrodes are metal plates used as negative & positive charge terminals. Material of construction of Electrode is graphite. Metal plates containing positive charge is known as Anode; negative charge possessing terminal known as Cathode. Electrodes are the conductor of electricity which comes in contact with electrolytic solution.
Mechanism of Electrolysis:
- Electrolysis mechanism is described below as per indicated figure. Please refer below:
- Let’s starts the electrolytic process with an example consist of Beaker in which Electrolyte solution AB is added to the beaker.
- After this two electrode placed corresponding to each other in the beaker. Left electrode is connected to the positive terminal of battery to known as Anode; whereas right electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery is known as Cathode.
- Electricity source Direct current (D.C Type) is provided through the battery arrange between two electrode in the beaker.
- After the connected electricity source to electrolytic solution, Electrolytic solution (AB) breakdown into A+ and B–.
At cathode end reduction takes place. Reduction is the process in which gains of electron. At cathode Electrode (right side), electrons coming from negative terminal of battery combines with A+ to form A. Finally deposition of A is takes place at the cathode Plate. Cathode is Position where deposition of cations takes place.
A+ + e– ——– A (Reduction Occur)
At anode end oxidation takes place. Oxidation is the process in which lose of the electron . At Anode Electrode (left side), electrons from B– travels towards the positive terminal of battery to make the circuit complete. Finally deposition of B is takes place at the anode Plate. Anode is Position where deposition of anions takes place
B– ——– B + e– (Oxidation Occur)
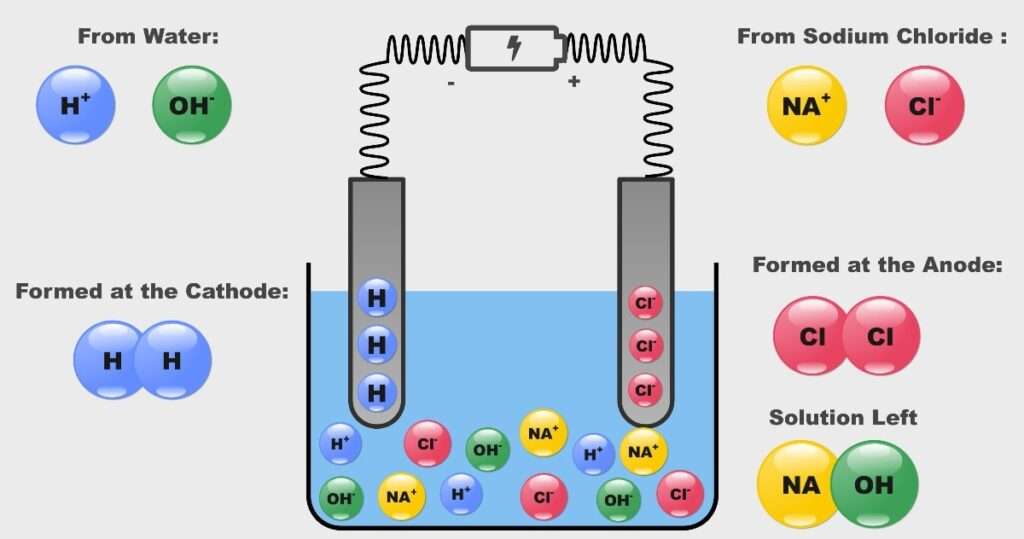
Electrolysis of Brine (Sodium Chloride & Water as an electrolyte Solution):
Let’s understand the same mechanism with the taking example of NaCl and H20 as electrolyte solution.
- Arrangement for the electrolyte process & Anode & cathode connections explained above remains same (battery Electricity source, electrode, beaker etc).
- Initially Sodium Chloride (salt) dissolve in water solution. As the electricity is supplied to the electrolyte solution starts to conduct electricity. NaCl & H2O is breakdown into Na+, Cl– and H2+ O– respectively.
- After conduction of electricity following reaction takes place
NaCl —– Na+ + Cl–
H2O —— H2+ + O–
At cathode reduction takes place, formation of H• takes place from H2+ and electron coming from battery negative terminal.
H+ + e– ——- H• (Reduction)
H• + •H ——– H2
Another H• which is formed at cathode to form H2 which is released through the process.
At anode Oxidation occurs, formation of Cl• takes place from Cl– and donates an electron towards the battery positive terminal.
Cl– ——- Cl + e– (Oxidation)
Cl• + Cl ——- Cl2
Another Cl• which is formed at anode to form Cl2 which is released through the process.
- Overall reaction takes places is following within the Electrolysis Process
H2O + NaCl —— H2 + Cl2 + NaOH
Uses of Electrolysis:
- Used in the production of Electricity, hence Generate about 98% of national consumption plays important role in to fulfill the Electricity Demand.
- Production of Gases (i.e. Hydrogen, Chlorine etc)
- Production of sulphuric Acid.
- Extraction of Copper from the ores.
- Refining of Aluminum.
- Treatment of Wastewater.
Source:- revisechemistry.uk






























