Types of Distillation
Types of distillation include simple distillation, Steam Distillation, Fractional Distillation and Vacuum Distillation.
Simple Distillation
Simple distillation can be used when the boiling points of two liquids are notably different from one another or to separate liquids from solids or nonvolatile mixers. In simple distillation, a mix is heated to change the foremost volatile component from a liquid into vapor. The vapor rises and passes into a condenser. Usually, the condenser is cooled (e.g., by running cold water around it) to market condensation of the vapor, which is collected.
Steam Distillation
Steam distillation is employed to separate heat-sensitive components. Steam is added to the mixture, causing a number of it to vaporize. This vapor is cooled and condensed into two different liquid fractions. Sometimes the fractions are collected separately, or they’ll have different density values, in order that they separate on their own. An example is steam distillation of flowers to yield volatile oil and a water-based distillate.
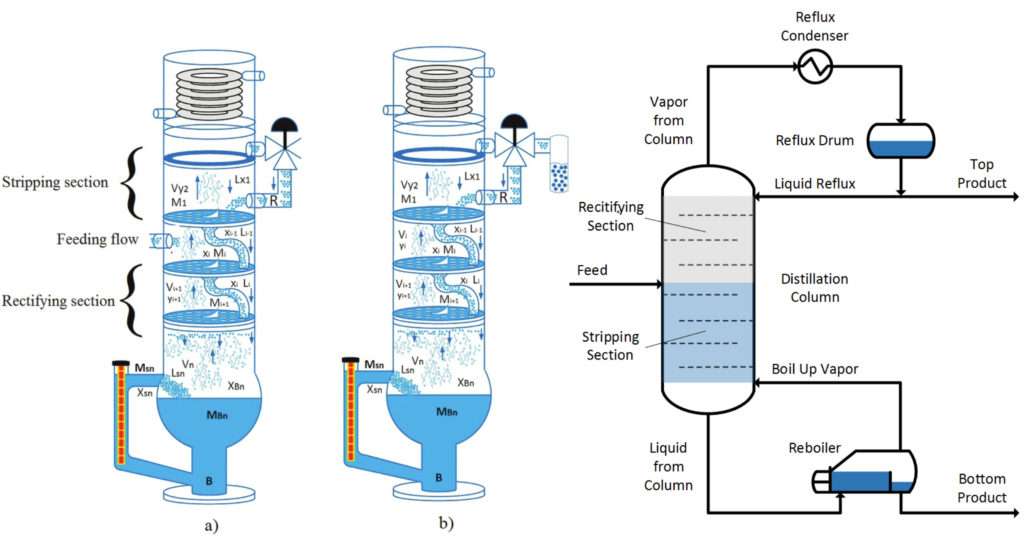
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is employed when the boiling points of the components of a mix are near to each other, as determined using Raoult’s law. A fractionating column is employed to separate the components using a series of distillations called rectification. In fractionation , a mix is heated so vapor rises and enters the fractionating column. because the vapor cools, it condenses on the packing of the column. the warmth of rising vapor causes this liquid to vaporize again, moving it along the column and eventually yielding a better purity sample of the more volatile component of the mixture.
Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation is employed to separate components that have high boiling points. Lowering the pressure of the equipment also lowers boiling points. Otherwise, the method is comparable to other types of distillation. Vacuum distillation is especially useful when the conventional boiling point exceeds the decomposition temperature of a compound.
Reference:- thoughtco
































