Vacuum Distillation | Vacuum Distillation Process
Vacuum Distillation | Vacuum Distillation Process
Introduction:
Water is available in basically every industrial process; it isn’t just utilized for manufacturing products, but additionally for different purposes accompanying the production process. Water is essential and fundamental in the production of practically any product, whether it is a vehicle or a toothpick. A vast amount of water is spent on the production of paper, food, and synthetic substances. This alleged industrial water generated in production processes is normally contaminated after the production process and polluted with heavy or weighty metals, oils, or salts among different substances of concern.
The contaminated water can cause extreme ecological damage assuming that it is returned to the public supply without being purified ahead of time. Subsequently, an efficient long-haul strategy is to purify or purge the contaminated water directly in the facility where it was produced since the contamination generally makes up just a small fraction of around 2-3% of the wastewater and the purified water can be reused directly in the facility too.
What is Vacuum distillation?
The wastewater is evaporated, the dirt stays behind, and the rising steam is liberated from impurities. The condensate, additionally called distillate, can be reused in production. Along these lines, 100 % wastewater produces around 98 % cleag and water and just 2 % residue, which can be disposed of at minimal expense. The underlying physical principle is named the Distillation of substances as per boiling point differences. Vacuum Distillation is a procedure or strategy of separating a blend of compounds at a pressure that is lower than the normal atmospheric pressure. By reducing their boiling point fully backed up by a vacuum. It is used in the different processes, for instance in Beverage and food production to extract plant substances or to separate long-chain hydrocarbons in Petroleum treatment facilities.
The vacuum distillation method additionally saves energy, since water evaporates under a vacuum at 80 degrees Celsius rather than 100 degrees Celsius. This significantly affects how much energy is consumed. In view of the utilization of heat exchangers as well as the reuse of the evaporation heat in the system, the set-up of a vacuum distillation consumes comparably small electricity. A vacuum distillation plant is suitable for the purpose that is exceptionally energy-saving in contrast to atmospheric evaporation.
How does vacuum distillation work?
In the vacuum distillation process, the industrial wastewater is taken care of into a heat exchanger and evaporated under vacuum. The heat exchanger comprises a bundle of tubes where the wastewater is divided into more modest volumes to make it easier to evaporate. The applied vacuum led then to a modification of the boiling over. This permits water to evaporate at around 185 degrees Fahrenheit (85 °C) rather than 212 degrees Fahrenheit (100 °C) under atmospheric pressure.
All substances with a higher boiling over than water remain in the evaporation residue. The resulting vapor is then taken care of in the vapor compressor. It creates compression heat, which warms up the steam to 248 degrees Fahrenheit (120 °C). From the vapor compressor, the compressed steam raises a ruckus around the tube bundle again where the cooler wastewater is taken care of, Condensing on the outer wall of the tubes. Subsequently, the steam returns to liquid clean water and can be released from the system or returned to the production process. The contaminated evaporation residue is then drained or depleted.
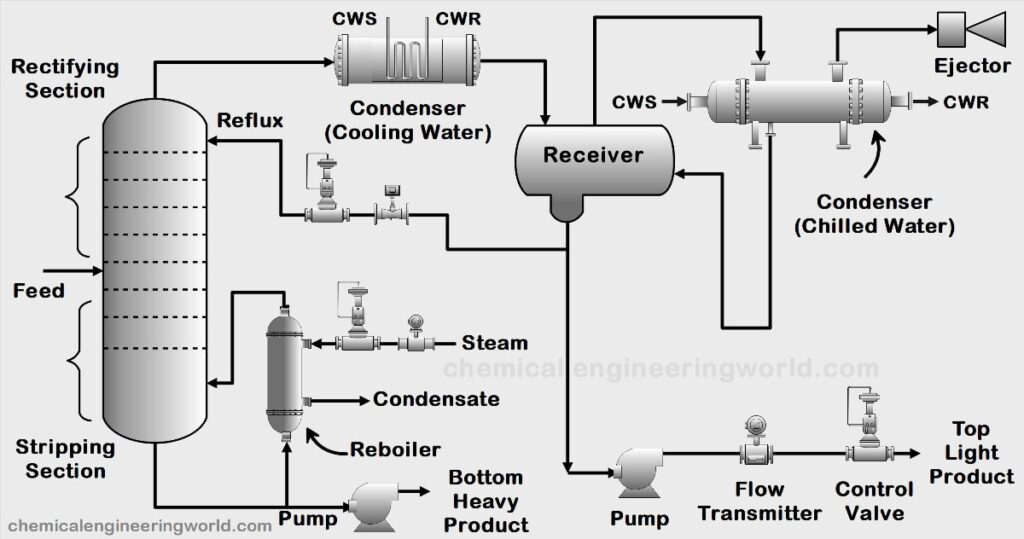
Pre–and after-treatment in the vacuum distillation process:
The heart or core of the wastewater treatment system is the vacuum distillation unit. Contingent upon the nature of the wastewater contamination, pre-treatment and post-treatment may be necessary.
1. The pre-treatment
Pre-treatment can include a belt filter or channel (or inclined belt filter), which is utilized to eliminate floatable and filterable solids from the water through a filter fleece selected to match the solids concentration and viscosity of the wastewater to be dealt with. Pre-treatment by a neutralization plant safeguards the microorganisms that break down organic substances in the wastewater, e.g., in the biological phase of a wastewater treatment plant. Microorganisms respond firmly to fluctuations in the pH esteem. In a neutralized plant, substances, for example, hydrochloric acid or caustic soda are many times used to produce a neutral liquid with a pH of 7 corresponding to that of water.
2. The after-treatment:
In the after-treatment, ultra-filtration can be utilized. In this process, the pores of the semipermeable layer (which can only be penetrated on one side) are more modest than in micro-filtration, however larger than in Nano filtration. In ultra-filtration, the treated dirty or grimy water is forced or constrained through plastic tubes at up to 10 bar bringing about particles, bacteria, and viruses being collected in the pores of the filter tubes. The outcome is totally germ-free water. The membranes are chiefly made of extremely minimal expense materials, for example, cellulose acetic acid derivations or polyamides.
What are the advantages of vacuum distillation Process?
Below we will look at some benefits of Vacuum Distillation:-
A. Lower Operating Temperatures:-
Heat-sensitive compounds are separated or isolated through the technique of vacuum distillation, minimizing or limiting the threat of thermal degradation or disintegrating.
B. Energy Efficiency:-
Operating or Working at lower temperatures can prompt energy savings, as less energy is required to heat the mixture to the lower boiling points accomplished under vacuum.
C. Increased Yield: –
Vacuum distillation expands the yield of desired items by dropping off the boiling points that works with the separation of higher-boiling compounds or mixtures that would some way or another stay in the deposition.
D. Pure and safe products:–
Vacuum distillation can produce unadulterated and safe products. The operation process is simple and requires less gadgets, bringing about high-quality products with high purity.
E. Reduced capital cost:–
Vacuum distillation can lessen the height and width of a distillation column, leading to reduced capital expenses. This makes it a savvy option, notwithstanding slightly higher operating costs.
What are the disadvantages of Vacuum Distillation Process?
Below we will discuss some limitations of Vacuum Distillation
A. Lower Operating Temperatures:-
Heat-sensitive compounds are separated or isolated through the technique of vacuum distillation, minimizing or limiting the threat of thermal degradation or disintegrating.
B. Energy Efficiency:-
Operating or Working at lower temperatures can prompt energy savings, as less energy is required to heat the mixture to the lower boiling points accomplished under vacuum.
C. Increased Yield:-
Vacuum distillation expands the yield of desired items by dropping off the boiling points that works with the separation of higher-boiling compounds or mixtures that would some way or another stay in the deposition.
D. Pure and safe products:–
Vacuum distillation can produce unadulterated and safe products. The operation process is simple and requires less gadgets, bringing about high-quality products with high purity.
E. Reduced capital cost:–
Vacuum distillation can lessen the height and width of a distillation column, leading to reduced capital expenses. This makes it a savvy option, notwithstanding slightly higher operating costs.
What are the disadvantages of Vacuum Distillation Process?
Below we will discuss some limitations of Vacuum Distillation
A. Equipment processing difficulty:–
Vacuum distillation equipment requires a moderate distance between the evaporating surface as well as the condensing surface. This can make the equipment dealing more inconvenient and excessive.
B. Solvent loss:–
During the activity of vacuum distillation, mixtures can be evaporated and solvents can be removed. The brief distance between the evaporation flask and the condenser can bring about solvent loss, which can be challenging to recover.
C. Higher cost:–
Vacuum distillation equipment is for the most part is costly compared to traditional distillation equipment. Accomplishing a high degree of vacuum requires high sealing performance of the materials utilized, which adds to the expense.
What are Vacuum Distillation Process Steps?
The Following steps mentioned below are as per the following:
- The diminished crude oil is pumped through a series of heat exchangers and a crude furnace until reaching the ideal temperature (350°C – 390°C).
- The decreased crude oil is flashed or blazed to separate the ideal fractions. Light vapors ascend to the top and heavier hydrocarbon liquid fall to the base.
- Steam injection at the lower part of the column works on the detachment of lighter boiling components.
- The vacuum column utilizes a series of pumps around to keep up with temperature at the right level at specific points along the tower.
- Light vapor gases are eliminated at the top of the tower, condensed, and reused back to the column as reflux. Light Naphtha is drawn off and an abundance of gases is sent to flare.
- Vacuum gas oil and greasing up(lubricating) oils are drawn off and coordinated for extra treatment in Hydro-treating units.
- Vacuum residue from the base is sent to intermediate storage or normally to be additionally processed in an FCC or delayed coking unit.
Where Vacuum distillation Process is mostly used?
A. Vacuum Distillation in Petroleum Refining:-
A complex combination of many different hydrocarbon compounds, petrol crude oil has a carbon atom count going from 3 to 60 carbon atoms for each molecule by and large, in spite of the fact that there might be small amounts of hydrocarbons beyond that reach. The most well-known approach to refining crude oil begins with the distillation of the incoming crude oil in an atmospheric distillation column, which operates at pressures fairly above atmospheric pressure to eliminate impurities.
It is critical not to subject the crude oil to temperatures over 370 to 380 degrees Celsius during the distillation process, since high molecular weight components in the crude oil will initiate thermal cracking and structure petroleum coke at temperatures higher than that. The formation or development of coke would achieve the plugging of the tubes in the furnace that heats the feed stream to the unrefined petroleum distillation section, which would make the column or section fizzle. Alongside the distillation column itself, plugging would likewise happen in pipping leading from the furnace to the column or section.
To accomplish good vapor-liquid contact, the internals of a vacuum distillation column should keep an extremely low-pressure increase from the highest point of the column to the lower part of the vessel. Along these lines, just products that are withdrawn from the side of the vacuum column are distilled using a distillation plate in a vacuum column. Most of the column packing material is utilized for the fume fluid reaching since pressing material has a lower pressure drop than distillation trays, which brings about a lower pressure drop. This packing material can be either organized sheet metal or randomly dumped packing, for example, Raschig rings, contingent upon the application.
B. Large-Scale Water Purification:-
Vacuum distillation is generally utilized in large industrial plants to eliminate salt from ocean water to produce new water. It is a productive technique for eliminating salt from ocean water. Desalination is the term used to depict this process. Subsequent to being put under a vacuum to bring down its boiling point, and having a heat source applied, the ocean water boils off and condenses, releasing fresh water. At the point when water vapor condenses, it keeps it from filling the vacuum chamber, taking into consideration the effect of running endlessly without a loss of vacuum pressure. The heat generated by the condensation of water vapor is taken out by a heat sink, which utilizes the incoming ocean water as a coolant, in this way preheating the ocean water that is taken care of into the system. A few sorts of distillation don’t utilize condensers, however, compress the vapor mechanically with a pump, which is referred to as vacuum distillation. Basically, this fills in as a heat pump, drawing heat from the vapor and permitting it to be returned to and reused by the incoming untreated water source subsequent to being concentrated. Various sorts of vacuum distillation of water are utilized today, with the most usually utilized being various distillation, Vapor-compression desalination, and multi-stage flash distillation being the most widely recognized.
Conclusion:-
It is the most common way of bringing down the pressure in a column or segment over an organic solvent to a level lower than the vapor pressure of the mixture, creating a vacuum, and causing the components with lower vapor pressure to evaporate from the mixture. The utilization of vacuum distillation can lessen the height as well as the diameter of a distillation column, as well as the general capital expense of the column.
Vacuum distillation is otherwise called “low-temperature distillation” or “low-pressure distillation.” The most common way of refining unrefined petroleum starts with the distillation of the incoming unrefined petroleum in an atmospheric distillation column, which operates at pressures somewhat above atmospheric pressure to eliminate impurities. Vacuum distillation is normally utilized in large industrial plants to eliminate salt from ocean water to produce fresh water. It is a proficient method of eliminating salt from ocean water.
Reference:- h2o-de, unacademy, schuf, kindle-tech