Rupture Disks Function
Rupture Disks Function :- A rupture disk could be a device designed to perform by the exploding of a pressure-retaining disk.
This assembly consists of a skinny, circular membrane typically fabricated from metal, plastic, or graphite that’s firmly clamped in a disk holder. Once the process reaches the exploding pressure of the disk, the disk ruptures and releases the pressure.

Rupture disks is put in alone or together with different kinds of devices. Once blown, rupture disks don’t reset; therefore, the complete contents of the upstream process equipment are ventilated.
Rupture disks are usually utilized in series (upstream) with a relief valve to stop corrosive fluids from contacting the metal components of the valve. Additionally, this mix could be a re closing system.
The
burst tolerances of rupture disks are
generally concerning ±5% for set pressures > forty psig.
Rupture Disk

Purposes of Rupture Disks
A rupture disk could be a sensitive relief device designed to rupture at a per-determined pressure and temperature. it’s a way of providing protection for personnel and equipment. As such, it should be a fail-safe device.
Rupture
disks are used wherever instant and full opening
of a pressure relief device is needed.
These devices also are used wherever “zero” leak-age is needed of a relief device. These devices also can be utilized in
series as “quick opening” valves.
Rupture disks is also used either in primary relief, in secondary relief, in series with a relief valve, or for alternative functions like “quick opening” valves.

Primary Relief
If used for primary relief, the rupture disk is that the solely device used for pressure relief. As such, it’s the benefits of being leak tight, a right away reaction time, minimum pressure drop, lowest price, terribly high re-liability, and minimum maintenance. it’s the disadvantage that it should get replaced once every rupture prevalence, and permits discharge till system pressure equals downstream pressure.
Secondary Relief
When utilized in a secondary relief capability, the rupture disk provides a backup vent to a primary relief device, sometimes a relief valve. Its purpose here is typically to produce extra protection against an unlikely however potential major event that might exceed the capability of the first relief device.
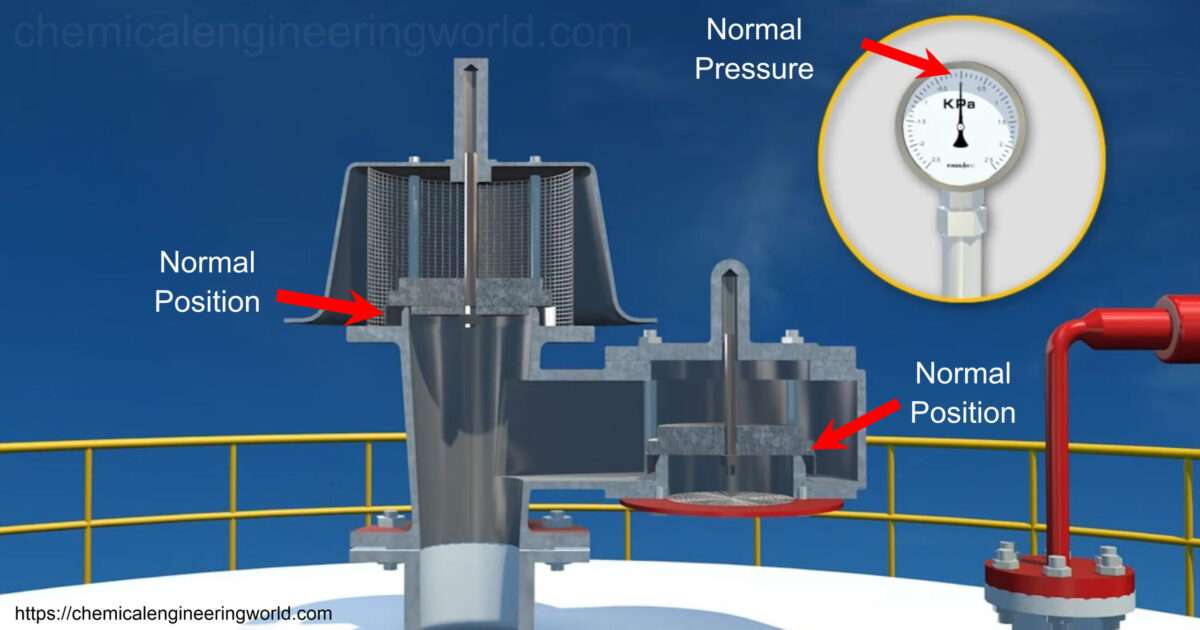
Rupture Disks Function In series with relief valve
When employed in series with a pressure relief valve, the rupture disk is typically put in upstream of the valve. The disk can shield the valve from method media that may corrode or plug it. The disk also can act as a seal, preventing any leak through the valve unless the disk is burst.
The area between the rupture disk and therefore the pressure relief valve should have a pressure gauge, try cock, free vent, or appropriate telltale indicator. the conventional configuration is an excess flow valve together with a pressure gauge. This arrangement is to eliminate the chance of, or facilitate the detection of, a back pressure build up. as a result of a disk responds to the differential pressure across it, it’ll not burst at its rated pressure if a back pressure is allowed to exist during this cavity.
A low-pressure rupture disk is used on the downstream aspect of a relief valve that discharges into a standard manifold to stop exposure of the valve to process or corrosive media discharging by the common manifold. The area between the relief valve outlet and therefore the rupture disk should be ventilated to stop the buildup of pressure that may adversely have an effect on the relief valve set pressure. An excess flow valve can fulfill for this feature.
Rupture Disks Other Functions
Due to the tiny inertia characteristics of a rupture disk, the gap time, i.e., from a closed and sealed condition to a full open condition, is a smaller amount than one half one msec (0.0005 sec.). This characteristic permits a rupture disk to perform as a “quick opening” valve.
Some samples of rupture disks used during this manner are: 1) shock tube operations; 2) unstable testing; 3) simulation of huge caliber gun discharges; 4) shifting of control mechanisms from a foreign location; 5) injection systems for suppression of upsets among storage vessels or systems.