Pressure Swing Distillation
Pressure Swing Distillation:- Pressure swing distillation is one of the methods which are employed in process and chemical industries to separate azeotropes. Azeotropes are liquid mixtures which when boiled gives no separation; it means the composition of components in the gas phase is equal to the composition of components in the liquid phase.
Not all liquid mixtures are azeotropes. Whenever a liquid is boiled it is often done at a constant pressure. In the temperature-composition diagram the point at which the bubble point curve and the dew point curve intersect is called the point of azeotropy. When ordinary distillation columns are used to treat such systems then the separation won’t take place even if an infinite number of stages are used.
Principle of Pressure Swing Distillation
At a constant pressure the mixtures that form azeotrope may have more than one point of azeotropy but it is quite common for azeotropes to have only one point of azeotropy.
Usually when pressure changes then the location of the point of azeotropy also changes. It means for same liquid mixture the composition at which the mixture forms an azeotrope is different for different pressures.
Since a change in pressure can alter relative volatility of the liquid mixture, for many azeotropes it is observed that if the pressure is changed to a certain level then the azeotropy disappears from the system. The system becomes completely zeotropic and it can be separated in a distillation column.
Operation of Pressure Swing Distillation
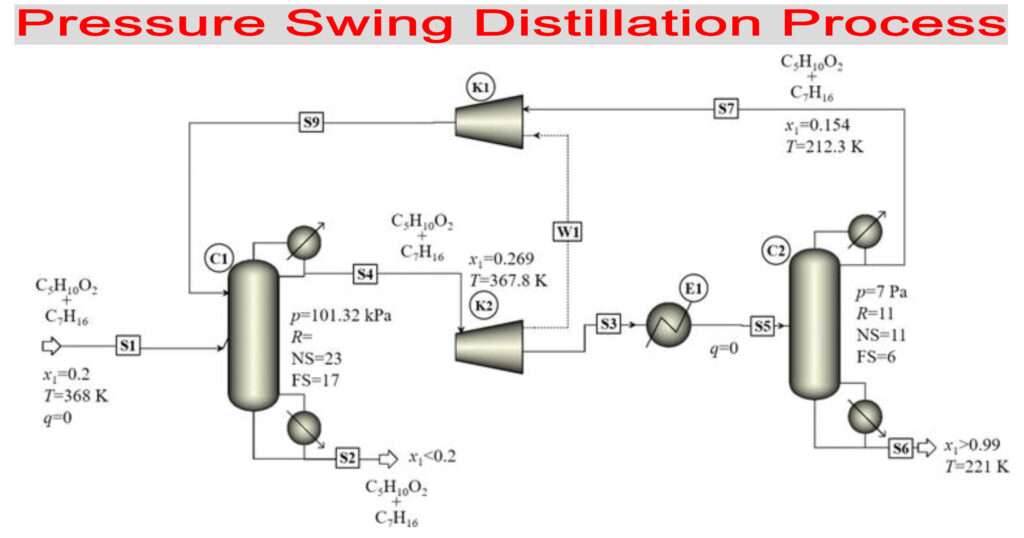
Pressure swing distillation does not utilise any additives; no extra component is added into the feed or the column in order to make changes in the liquid mixture. In the continuous operation, the separation is performed using two columns which are maintained at two different pressures.
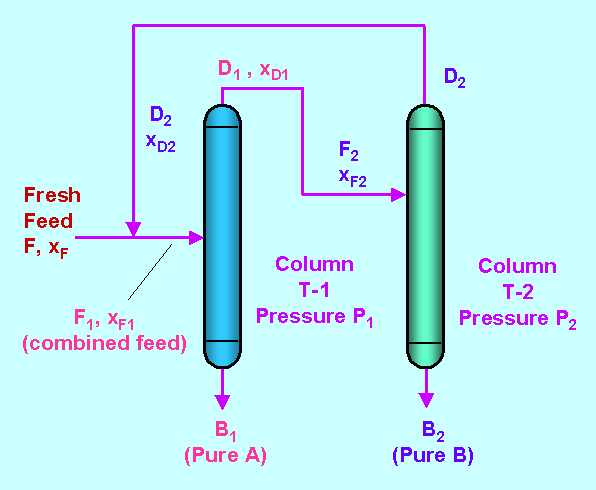
The first column is maintained at a low pressure and the second column is maintained at a high pressure. The distillate from second column is recycled and fed back to first column.
Suppose we have to separate a liquid mixture of two components; A and B.
The temperature composition diagram of the mixture at pressures P1 and P2 looks like this:
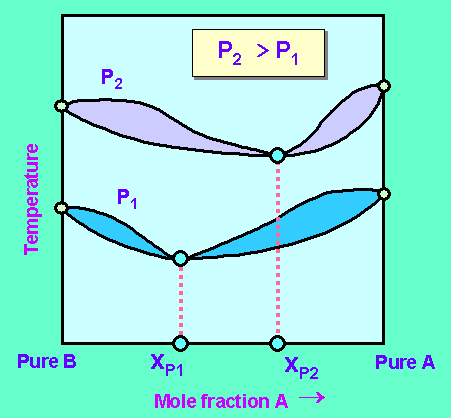
The point of azeotropy at pressure P1 is given by XP1 and point of azeotropy at pressure P2 is given by XP2.
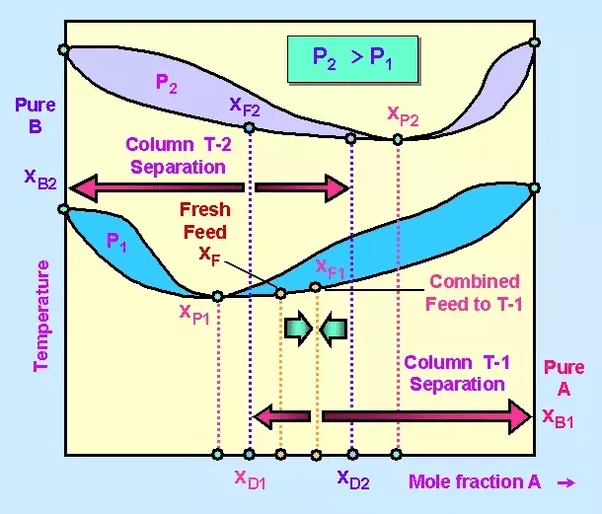
Before the feed is charged into the first column it is mixed with distillate of the second column. The composition of the distillate of the second column, D2 has a composition of XD2. This composition is closer to but not equal to the point of azeotropy XP2. It means the distillate mixture from the second column is not an azeotropic mixture.
The distillate obtained from first column, D1 has a composition XD1. This composition is also closer to but not equal to point of azeotropy XP1. It means the distillate mixture obtained from first column is also not an azeotropic mixture.
In this way the columns are operated at points closer to but not equal to the point of azeotropy and the result is that, Pure A is obtained as bottoms product from first column and Pure B is obtained as bottoms product from second column.
Some examples of azeotropes separated this way are acetone-methanol, ethanol-ethyl acetate, aniline-octane, propanol-toluene etc.
Advantages of Pressure Swing Distillation
- No additional material is needed hence any challenges to deal with cost, availability or usage of a substance is also eliminated.
- High Energy Savings are observed in continuous operations because heat transfer can be optimized by utilizing heat integration.
- Low initial investment cost as the size of columns required is relatively smaller.
Disadvantages of Pressure Swing Distillation
- To properly design the system, accurate equilibrium and azeotropic data are needed.
- The control structure and automation needed to design the system is quite complex.
- If the azeotropes are low boiling in nature then there is a possibility that the product may not be pure, it may be contaminated with high boiling components.
Source:- separationprocesses, intechopen