Gas Absorption Process
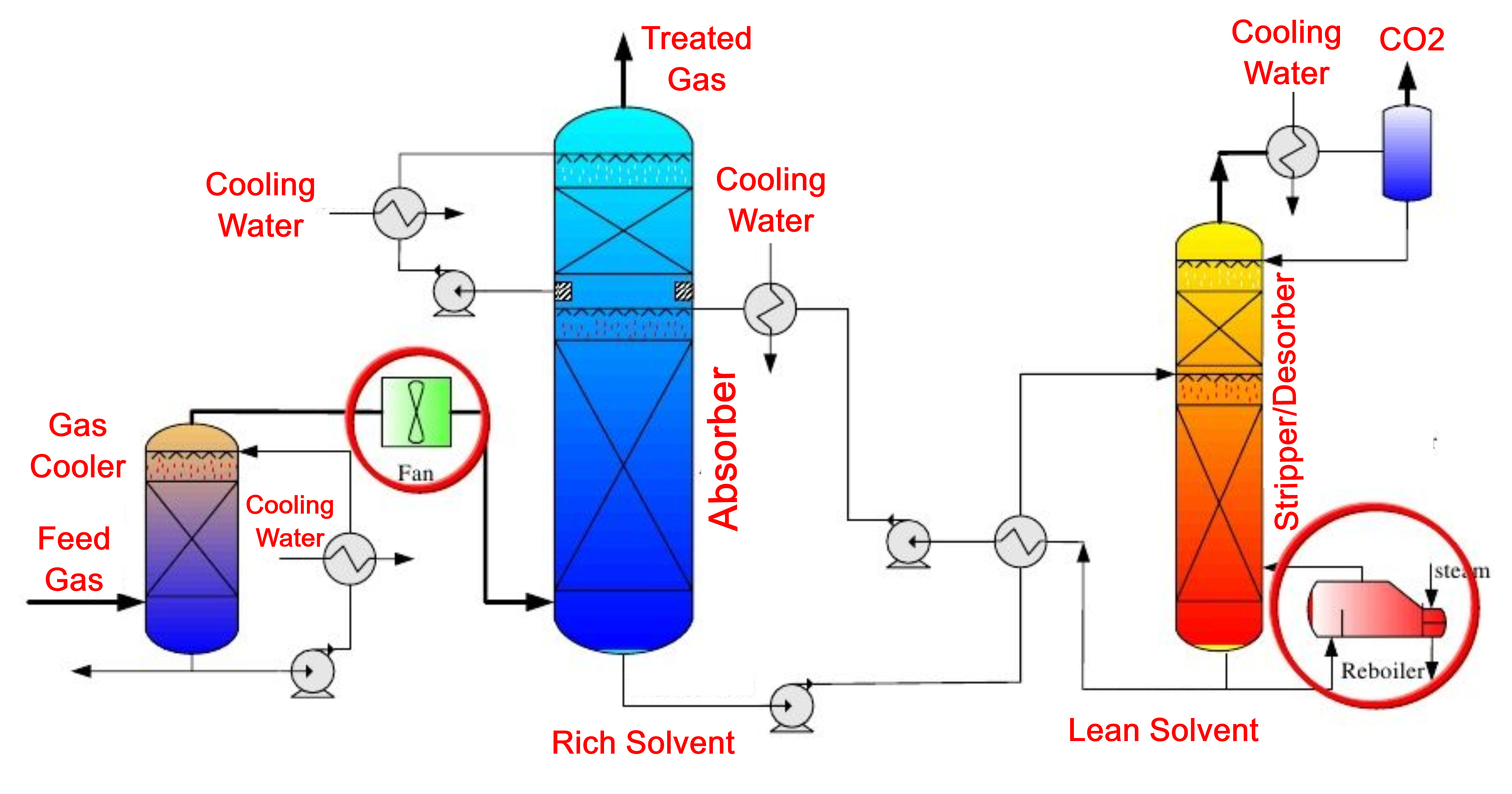
Gas Absorption Process:– In the Absorption process, we have a feed which is a mixture of various gases. This Gas mixture is contacted with a liquid which is called a solvent. When the contact takes place, mass transport of the component or components of interest takes place from the Gas phase to the Liquid phase. Absorption is a Gas-Liquid operation.
When any two phases are contacted with each other and if both the phases contain some components then practically all the components will get distributed in such a way that there will be some amount of each component in both the phases. If we contact a Gas phase and a Liquid phase then it is possible that not only components are transported from Gas phase to Liquid phase but also from Liquid phase to Gas phase; this is minimized or eliminated in absorption process by choosing an appropriate solvent which is pure and low in volatility.
Equilibrium Solubility of Gases in Liquid
Suppose we have a Liquid which fills a closed space partially, we fill the rest of the space with a Gas and allow them to contact each other. Assuming only Gas dissolves in the Liquid and the Liquid has negligible volatility; the process of mass transfer will occur inside the closed space.
Depending on the temperature of the system, not all gas will get dissolved in the liquid, only a specific amount of gas will get dissolved in the liquid. This specific amount of the dissolved gas when expressed in units of concentration or composition at a given temperature is called equilibrium solubility of the gas in liquid.
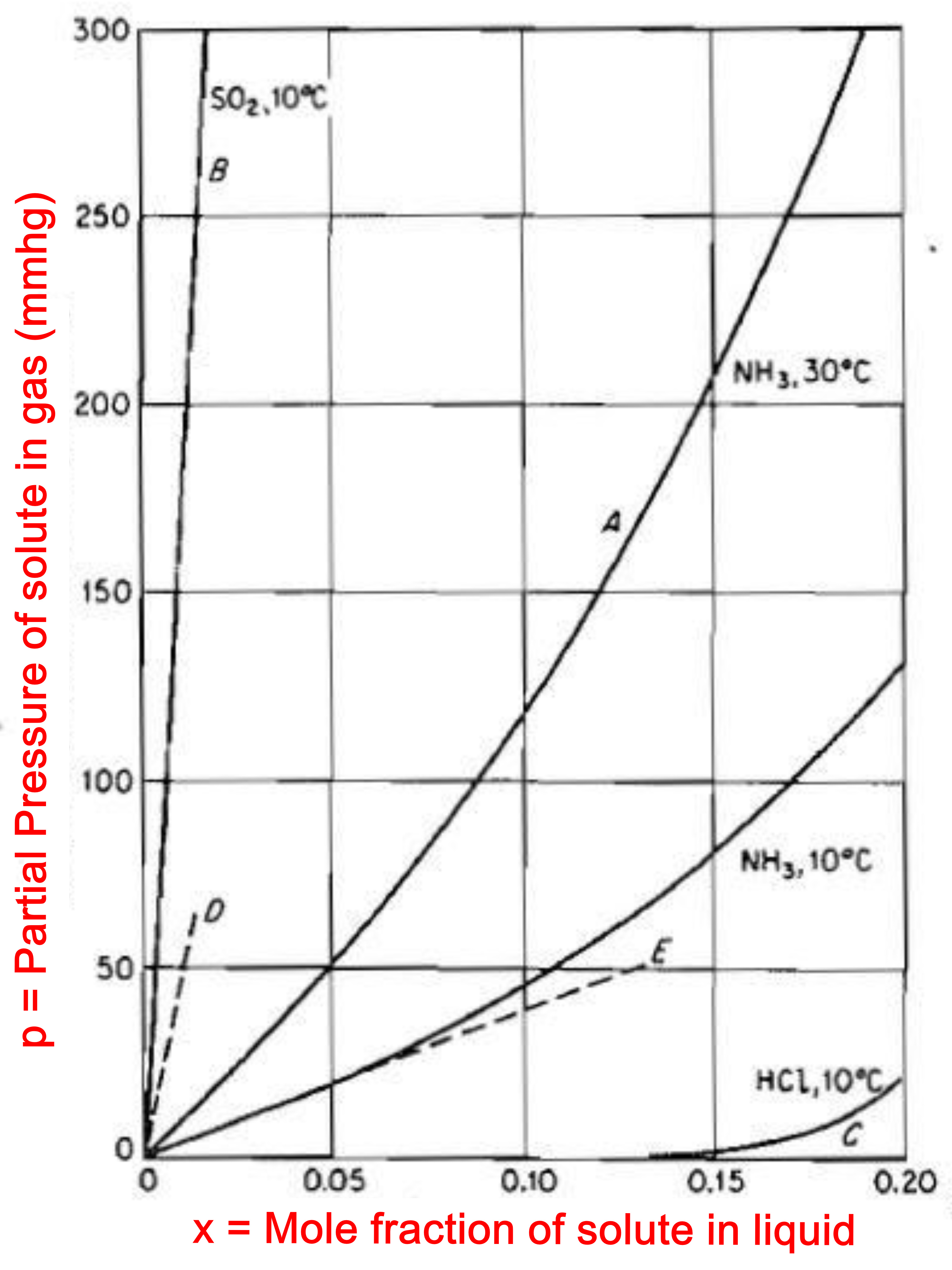
If we increase the temperature of the system then the kinetic energy of the molecules will increase, it means the activity of motion between the molecules will increase, this will cause some Gas molecules to get escaped from the Liquid. Thus, an increase in temperature increase the solubility of the Gas in Liquid and a decrease in temperature decreases the solubility of Gas in Liquid. This effect is seen in the Figure.
After the mass transfer is finished for this case of changed temperature, the new solubility value will be different than before.
The solubility value is also called as equilibrium value. An equilibrium curve for a particular temperature is obtained by varying the amount or pressure of the Gas and determining how much of the Gas has dissolved in the liquid.


